Why Medical Software Localization Is Unique

Unlike e-commerce, gaming, or general apps, medical software localization carries zero tolerance for error. Because it directly affects patient safety and clinical decisions, every word, unit, and workflow must be precise, compliant, and culturally adapted.
1. Regulatory Standards Define the Market
Medical software must comply with strict regulatory requirements in every target market:
- HIPAA (U.S.) for patient data privacy.
- MDR (EU) for medical device regulation.
- ISO 13485 for global quality management systems.
- Local regulations such as ANVISA in Brazil, NMPA in China, or Health Canada.
Failing to align with these frameworks can delay product launches, trigger costly rework, or even lead to rejection in new markets. For example, The European Medicines Agency’s 2022 Annual Report highlights that labeling issues, such as missing or incorrect information, continue to play a role in product recalls and compliance actions across the healthcare system. Similarly, Sedgwick’s recall index shows that EU medical device recalls increased overall in 2022, with labeling and documentation problems among the recurring causes.
2. Patient Safety Relies on Accuracy
A mistranslation in medical terminology isn’t just a usability issue — it can cause diagnostic errors, mistreatment, or fatalities. Research shows that 80% of medical errors stem from miscommunication. This makes medical translators and subject-matter experts indispensable in the localization process.
3. Cultural Adaptation Shapes Trust
Healthcare is cultural. Symbols, colors, and even icons vary in meaning across regions.
Without cultural adaptation, even perfectly translated software may fail to gain user trust. Unlike most industries, medical localization is not just a matter of communication — it’s a matter of life, safety, and compliance.
Key Elements of Medical Software Translation
When it comes to medical software localization, the margin for error is close to zero. Unlike typical apps, every detail in healthcare technology can directly affect clinical outcomes, compliance, and patient trust. Here’s a deep dive into the elements that demand the most attention:
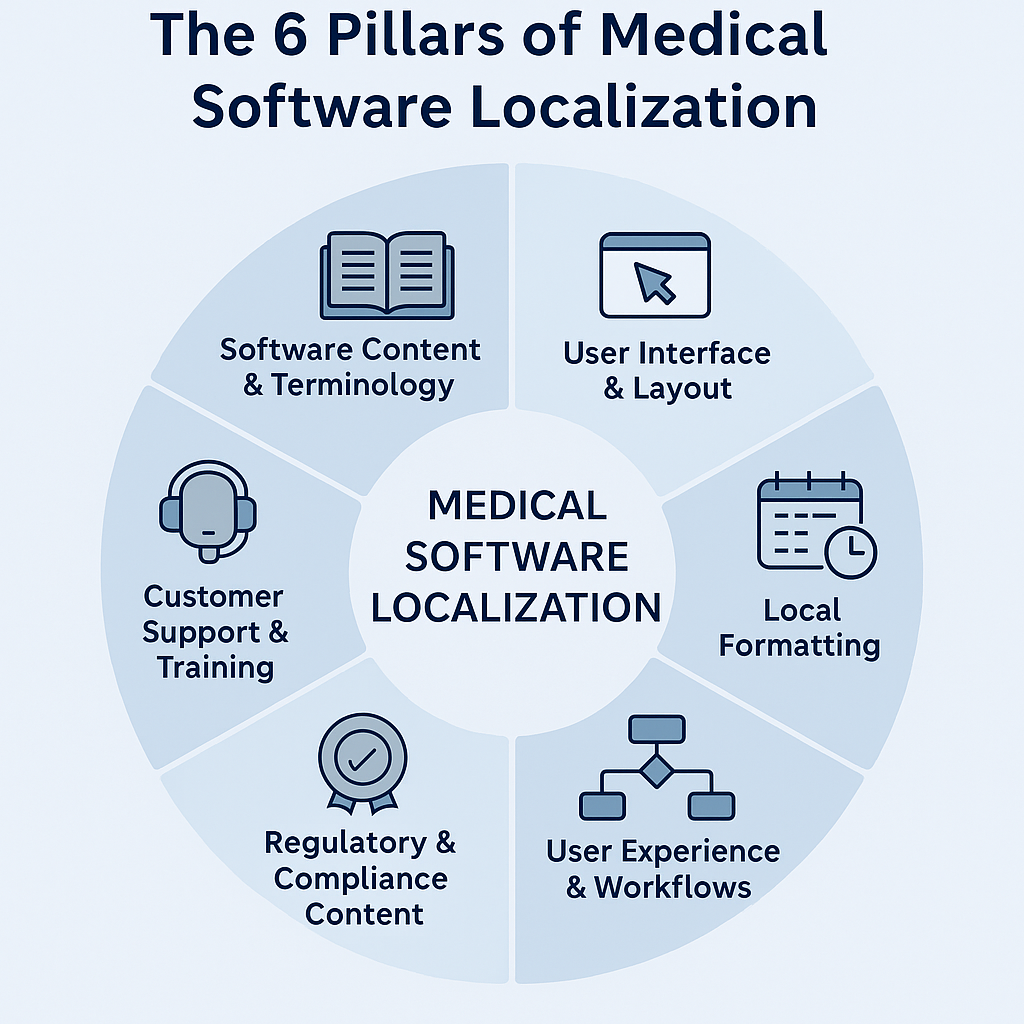
1. Software Content & Medical Terminology
Medical software contains thousands of strings — instructions, alerts, labels, and diagnostic references — all of which must be localized with precision. Generalist translators aren’t enough. Instead, businesses must rely on medical translators who understand terminology in context, supported by translation memory and standardized glossaries.
- Example: The English term “angina” may translate into multiple terms in Spanish, depending on whether it refers to chest pain (angina de pecho) or throat infection (angina de garganta). Without context, mistranslation could confuse both patients and doctors.
- Risk: A mistranslated dosage instruction could lead to under- or overdosing.
✅ Best Practice: Use a terminology management system that is reviewed by medical experts to ensure terms are consistent across updates.
2. User Interface (UI) & Layout
A localized UI is more than swapped-out text. It requires redesigning menus, adapting symbols, and ensuring readability across languages. Text expansion in German can increase character count by up to 35%, while Chinese may contract text by 20%. This impacts button sizes, menus, and instructions.
- RTL adaptation: Arabic and Hebrew require mirrored layouts, including navigation bars, input fields, and even progress indicators.
- Iconography: A checkmark means “correct” in many markets but has no meaning in Japan, where a circle (○) represents approval.
✅ Best Practice: Design “flexible UI frameworks” early in development to handle multilingual adjustments without breaking the software.
3. Local Formatting: Dates, Units & Measurements
Formatting errors are not cosmetic in medicine — they can be fatal.
- Dates: 06/07/2025 means June 7th in the U.S. but July 6th in Europe.
- Decimals: A comma vs. a period can transform 5.5 mg into 55 mg — a tenfold dosage error.
- Units:
- Blood glucose: mg/dL (U.S.) vs. mmol/L (EU).
- Temperature: Fahrenheit (U.S.) vs. Celsius (most other markets).
✅ Best Practice: Always include unit localization logic in software design and run cross-market testing with clinicians to catch risks early.
4. User Experience (UX) & Workflows
Healthcare professionals operate in high-stakes, time-sensitive environments. If a localized workflow feels unnatural, it can delay diagnosis or treatment.
- Navigation: In cultures that read right-to-left, users expect navigation to start from the right. If ignored, it slows down critical input.
- Error messages: A vague prompt like “Invalid entry” might confuse non-English users; a localized version should specify the error clearly (e.g., “Blood pressure value must be between 40–250 mmHg”).
✅ Best Practice: Conduct user testing with healthcare professionals in each target market to validate UX against clinical workflows.
5. Regulatory & Compliance Content
In medical software, compliance text is just as important as the code itself. Every privacy policy, consent form, and disclaimer must meet regulatory requirements in each market.
- U.S.: HIPAA for data privacy, FDA approval for medical software devices.
- EU: MDR + country-specific language requirements for labeling.
- China: NMPA requires 100% Mandarin — a single untranslated string can block approval.
- Brazil: ANVISA requires localized documentation aligned with national standards.
✅ Best Practice: Involve compliance experts during localization, not after — regulatory debt is expensive to fix.
6. Customer Support & Training Materials
Localization doesn’t end at the product interface. Patients and healthcare professionals need multilingual support that aligns with the software.
- Support channels: FAQs, chatbots, and call centers must operate in local languages.
- Multimedia: Video tutorials require dubbing, subtitling, or voiceovers. Accessibility features (screen readers, alt text, captions) must also be localized.
✅ Best Practice: Pair translation services with cultural adaptation to make support resources relatable, not just readable.
Key Takeaway: Truly effective localized medical software isn’t just text-perfect. It’s adapted across content, design, regulation, and support — ensuring patient safety, compliance, and user trust in every market.
Best Practices for Medical Localization
To ensure safety, compliance, and scalability, companies should follow these core practices:
- Integrate Early
- Build localization into the development workflow from the start.
- Externalize UI strings, design flexible layouts, and align with local regulatory requirements before launch.
- Adapt Culturally
- Go beyond translation to address visuals, colors, symbols, units, and tone.
- Ensure the software feels natural to the target audience and avoids cultural missteps.
- Involve Experts
- Engage medical translators, clinicians, and compliance specialists.
- Validate terminology, workflows, and regulatory texts with in-market experts to ensure accuracy.
- Test and Leverage Technology
- Run linguistic, functional, and regulatory QA with real users.
- Use translation memory, terminology management, and continuous localization to scale globally.
These best practices are simple but vital — plan early, adapt culturally, validate with experts, and test rigorously. This balance protects patients and ensures global readiness.
Your Next Steps to Medical Software Localization
When medical software localization is done right, it safeguards patients, ensures regulatory compliance, and builds credibility with healthcare professionals. Companies that plan localization early, adapt to cultural and linguistic nuances, and adopt continuous workflows are not just avoiding risk — they’re accelerating safer, more effective global rollouts.
The difference lies in expertise. By partnering with specialists in medical software translation and medical localization services, businesses can navigate terminology challenges, meet regulatory requirements, and deliver software that works seamlessly in every target market. If you’re preparing to expand globally, now is the time to make localization a core pillar of your strategy.






