Language barriers in healthcare are more than a communication challenge when patient safety is at stake. They can be the difference between effective treatment and serious medical errors.
It’s why language access becomes a responsibility and imperative. Every hospital and clinic serving diverse communities needs reliable healthcare interpretation services to ensure accurate, compassionate, and compliant care.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know: what healthcare language services are, why they’re critical, which types to consider, and best practices to integrate them into your operations. Whether you’re building your program from scratch or refining an existing system, this is your starting point for delivering safe, equitable care to every patient, in every language.
What Are Healthcare Interpretation Services?
So, what exactly is healthcare interpretation, and what do interpreters in healthcare do?
At its core, healthcare interpretation is the process of facilitating verbal communication between patients with limited English proficiency (LEP) and healthcare professionals.
This sensitive field demands more than literal word translation; it requires real-time communication of meaning, cultural subtleties, and emotional impact. This ensures that medical information is accurately exchanged, from symptoms and diagnoses to treatment plans and consent forms, all for truly effective communication.
What Are the Different Types of Healthcare Interpretation Services?
Types of Healthcare Interpretation Services?
Healthcare facilities employ various methods to provide this essential service, each with its advantages.
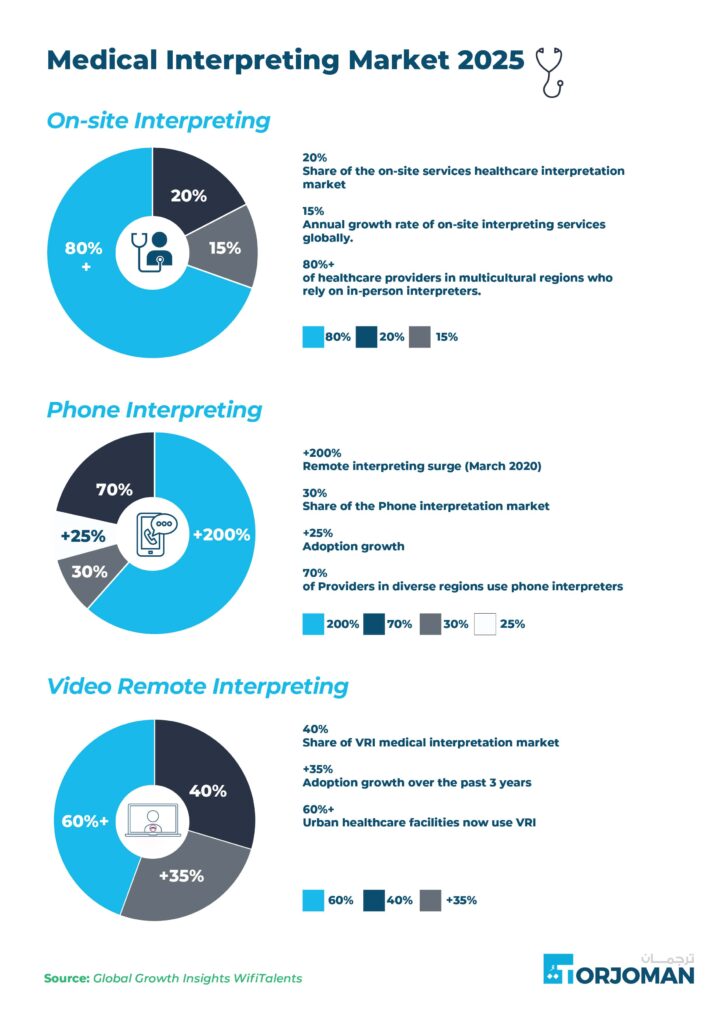
A. In-Person/On-Site Interpreting
This is the traditional approach, where a professional interpreter is physically present with the patient and healthcare provider. It’s particularly valuable in high-stakes or emotionally sensitive situations such as oncology consults, labor and delivery, mental health evaluations, or end-of-life discussions.
Although digital solutions have grown rapidly, on-site interpretation still makes up about 20% of the healthcare interpretation market, growing approximately 15% annually. In fact, over 80% of healthcare providers in multicultural regions continue to rely on on-site interpreters.
However, it often requires advanced scheduling, travel time, and minimum-hour charges, which can make it less accessible in rural or fast-paced clinical environments.
B. Phone Interpreting (Over-the-Phone Interpreting OPI)
Over-the-phone interpretation (OPI) offers real-time language support, where patients and providers access an interpreter over a telephone line. This offers immediate, remote multilingual interactions, often more cost-effective and ideal for remote areas. You’ll often find phone interpreting used for scheduling appointments, quick triage calls, medication instructions, and follow-up questions.
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically accelerated the adoption of remote interpreting solutions, with usage surging by over 200% by March 2020. As a result, audio interpretation services now account for approximately 30% of the global healthcare interpretation market, with a 25% increase in adoption reported in 2025. Now, 70% of healthcare providers in multicultural regions rely on phone interpreters for quick access to language support in fast-paced or resource-limited environments
C. Video Interpreting (Video Remote Interpreting – VRI)
Video remote interpreting connects patients and providers with an interpreter via a video call on a tablet, computer, or smartphone. This method combines the visual advantages of in-person interpreting (allowing for visual cues and facial expressions) with the immediacy and accessibility of phone interpreting.
It’s now the fastest-growing format in the healthcare interpreting space. In 2025, a growing preference for VRI was indicated in specific medical settings, such as a neuroradiology procedure at Mount Sinai Hospital, where video remote interpreting healthcare with American Sign Language was crucial.
VRI currently represents 40% of the medical interpretation market. Adoption has grown by 35% over the past three years, and today, more than 60% of urban healthcare facilities have integrated VRI into their operations, leveraging its speed, visual clarity, and convenience to support diverse patient populations.
| Feature/Type | In-Person/On-Site Interpreting | Phone Interpreting | Video Interpreting (VRI) |
| Presence | Physically present | Audio only (over phone line) | Visual and audio (via video call) |
| Accessibility | Limited by interpreter availability and travel | Excellent (24/7, vast language pool, remote areas) | Excellent (combines visual with remote access) |
| Best For | Sensitive conversations, complex procedures, sign language users, and situations requiring strong rapport | Scheduling, quick triage, medication instructions, follow-up, and less common languages | ER visits, initial assessments, consultations with visual demonstrations, and sign language users |
| Key Limitation | Less accessible, higher cost | Lack of visual cues can hinder nuanced communication | Requires technology and a stable internet connection |
Why Hospitals and Clinics Need Healthcare Interpreting?
1- Language and Communication Barriers
Our world is more connected than ever. Many regions and countries, including the US, Europe, and the GCC, are wonderfully diverse, with populations speaking hundreds of languages. In the US alone, over 22% of residents speak a language other than English at home, a 192% increase between 1980 and 2018. In hospitals, however, diverse backgrounds can pose a risk when patients can’t describe their pain and doctors can’t explain risks.
When patients have limited English proficiency, simple conversations can become complicated, leading to serious misunderstandings. This isn’t just an inconvenience; it can cause wrong diagnoses, medication mistakes, and a general loss of trust.
When there’s a language barrier, studies show patients are much more likely to be confused about how to use their medication (almost 35% more often). This also leads to nearly 16% suffering from harmful reactions due to not understanding. Using the correct medical terms is crucial for effective communication.

The GCC and the Middle East is no exception.
In the UAE, up to 97% of healthcare staff are expatriates, primarily from South or Southeast Asia. However, many local patients aren’t fully fluent in English. This often creates a communication gap at the point of care, and doctors and nurses are then reluctant to rely on unofficial interpreters, family members, or gestures, which can easily lead to misunderstandings that put patients at risk.

2- Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Providing healthcare interpretation isn’t just a kind gesture; it’s legally mandated. Hospitals and clinics that don’t follow these rules risk significant fines and the loss of crucial federal funding.
Examples of Regulations:
- United States:
- Title VI of the Civil Rights Act (1964): Bans discrimination based on national origin by entities receiving federal funding—this includes providing language access to LEP (Limited English Proficient) patients.
- Executive Order 13166 (2000): Requires federal agencies and federally funded healthcare providers to ensure meaningful access to services for LEP individuals.
- Section 1557 of the Affordable Care Act (ACA): Prohibits national origin discrimination in any federally funded health program. Mandates the use of qualified interpreters and free, timely language support, extending to digital content by 2025.
2. GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council):
- GCC nations like the UAE regulate the translation profession through laws like the Federal Decree on Translation (2022), which requires licensing, fluency, and ethical standards.
- While healthcare isn’t consistently named, the law supports professional language access in critical sectors, especially important in this highly multilingual region.
3- Better Patient Experiences: Safety and Satisfaction
When patients feel understood about their care, they’re more likely to trust their providers, adhere to treatment plans, and return for follow-up care.
This has a measurable impact on patient satisfaction and trust in care. In one study, only 52% of non-English-speaking patients reported being satisfied with their emergency department experience, compared to 71% of English-speaking patients. Additionally, 14% of non-English speakers said they would not return to the same emergency department for future care, versus 9.5% of English speakers, signaling a loss of patient confidence tied directly to language access.

Another study focused on Spanish-speaking Hispanic patients in San Bernardino, California, found that 97% of patients expressed increased satisfaction when their provider spoke Spanish, and 83.7% said provider fluency in Spanish was important to them.
The study concluded that language concordance significantly improves patient satisfaction, and highlighted the potential risk: lower satisfaction due to language discordance may contribute to adverse patient outcomes, a critical concern that warrants closer attention from healthcare systems.

Best Practices for High-Quality Interpretation in Healthcare
Delivering safe, respectful, and effective care begins with clear communication, which means making professional language access a non-negotiable part of your healthcare operations. The following best practices aren’t just checkboxes; they’re foundational pillars that help build trust, improve outcomes, and mitigate the risks associated with language gaps. Partnering with qualified, locally informed interpretation providers is essential to doing this right.
A. Strategic Planning: Develop a Language Access Plan (LAP)
Every healthcare facility needs a clear, actionable Language Access Plan (LAP) to ensure patients receive care in a language they fully understand. Without it, language access becomes inconsistent, reactive, and risky.
Here’s what a solid LAP includes:
- Know Your Community: Map the languages commonly spoken by your patients. This helps allocate interpreting resources where they’re needed most.
- Set Clear Access Points: Define how staff can quickly connect with interpreters—whether in person, over the phone, or via video remote interpreting (VRI). Speed and ease of access are critical in clinical settings.
- Translate Key Documents: Consent forms, aftercare instructions, and medication guidelines must be available in the most common languages your patients speak, using certified medical translators, not
- generic tools or ad-hoc translations.
B. The Right People: Prioritize Qualified, Certified Interpreters
Language is complex, especially in medicine, where a single misinterpreted term can impact a diagnosis, treatment, or even a life. That’s why interpretation should never be left to chance, and certainly never to untrained individuals.
A Weill-Cornell Qatar study found that Arabic-, Hindi-, and Urdu-speaking patients in Qatar often faced significant challenges accessing care due to language barriers. Many of them ended up relying on family members, nurses, or other untrained individuals to interpret. The result? Miscommunication, delayed care, and frustration on all sides.
This is a clear call to action:
- Only work with professional medical interpreters—those trained not just in the languages, but in clinical terminology, patient privacy, and cultural sensitivity.
- Insist on certification from reputable bodies like the CCHI or NBCMI, and make sure your language partners maintain these standards across their interpreter pool.
- Build relationships with established local interpretation companies who understand your regional context and patient population. They bring not just language fluency, but the cultural familiarity essential for patient-centered care.
C. Smart Tools: Leverage Technology Wisely
Technology can be a powerful enabler, but only when used in support of trained professionals. Think of it as a bridge, not a substitute.
- Real-Time Access: Platforms that offer on-demand phone or video interpretation can fill critical gaps, especially in emergencies or after hours.
- Security First: All tools should comply with healthcare data protection laws and ensure confidentiality at every step. Don’t compromise patient trust by using insecure or unfamiliar solutions.
D. Beyond Words: Cultivate Cultural Competency
Accurate understanding goes beyond literal translation. It requires cultural fluency—being able to recognize and respect the values, beliefs, and communication styles that shape how a patient receives care.
- Train All Staff: Equip everyone, from reception to physicians, with the cultural tools to serve diverse communities better.
- Work in Sync with Interpreters: Teach staff how to engage effectively with interpreters—maintaining eye contact with patients, using short and clear sentences, and allowing space for interpretation.
E. Continuous Improvement: Evaluate and Adapt
Language access is never “done.” It must be refined constantly based on real-world feedback and changing patient demographics.
- Ask for Feedback: Regularly gather insights from patients and frontline staff on interpreter experiences.
- Act on Data: Use feedback to revise your LAP, retrain staff, or reevaluate your interpreting partners.
Time to Act: Integrate Medical Interpreting Services for the Safety of Your Local Patients and the Integrity of Your Business
When patients are at their most vulnerable, communication must be clear, compassionate, and precise. That’s why professional healthcare interpretation is an ethical responsibility and a business necessity.
Torjoman’s healthcare interpretation services are built to meet this need, with certified interpreters who bring cultural fluency and medical expertise to every interaction. Whether you’re navigating complex diagnoses or sensitive care conversations, our team ensures language is never a barrier to healing.
For healthcare providers seeking trusted interpretation services in Dubai and across the region, Torjoman offers local insight, global standards, and a deep commitment to patient-centered care.






